

Each file will contain search strings with each string on a separate line in the file.When any of the strings match any part of the absolute path of the file to be copied, that file will be excluded from being copied.

The Destination file system can be FAT or NTFS.Ĭopies file ownership and discretionary access control list (DACL) information.Ĭopies file audit settings and system access control list (SACL) information (implies /o). n is required when you copy files or directories from an NTFS volume to a FAT volume or when the FAT file system naming convention (that is, 8.3 characters) is required on the Destination file system.
EMCOPY POWERSHELL HOW TO
For information about how to set the archive file attribute by using attrib, see Additional References.Ĭreates copies by using the NTFS short file or directory names.
Unlike /a, /m turns off archive file attributes in the files that are specified in the source.
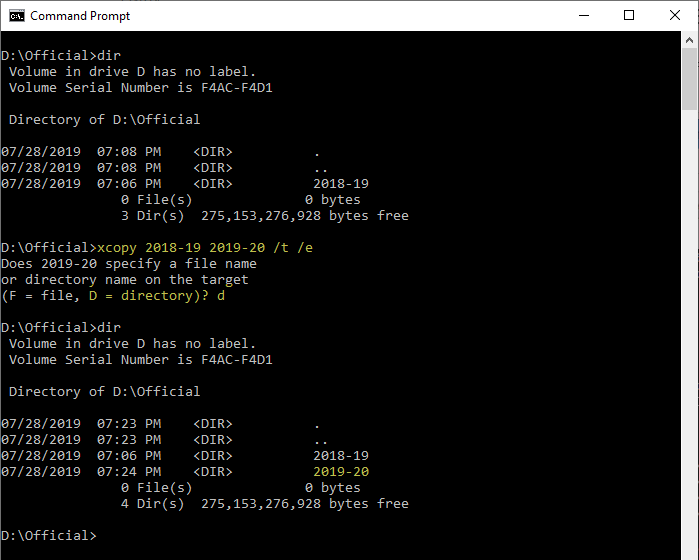
For information about how to set the archive file attribute by using attrib, see Additional References.Ĭopies Source files that have their archive file attributes set. a does not modify the archive file attribute of the source file. By default, xcopy does not copy hidden or system filesĬopies only Source files that have their archive file attributes set. By default, xcopy removes the read-only attribute.Ĭopies files with hidden and system file attributes. To copy empty directories, you must include the /e command-line option.Ĭopies files and retains the read-only attribute on Destination files if present on the Source files. Use /e with the /s and /t command-line options.Ĭopies the subdirectory structure (that is, the tree) only, not files. If you omit /s, xcopy works within a single directory.Ĭopies all subdirectories, even if they are empty. By default, xcopy prompts you to specify whether Destination is a file or a directory.Ĭopies directories and subdirectories, unless they are empty. Then, xcopy copies all specified files into the new directory. If Source is a directory or contains wildcards and Destination does not exist, xcopy assumes Destination specifies a directory name and creates a new directory.
EMCOPY POWERSHELL UPDATE
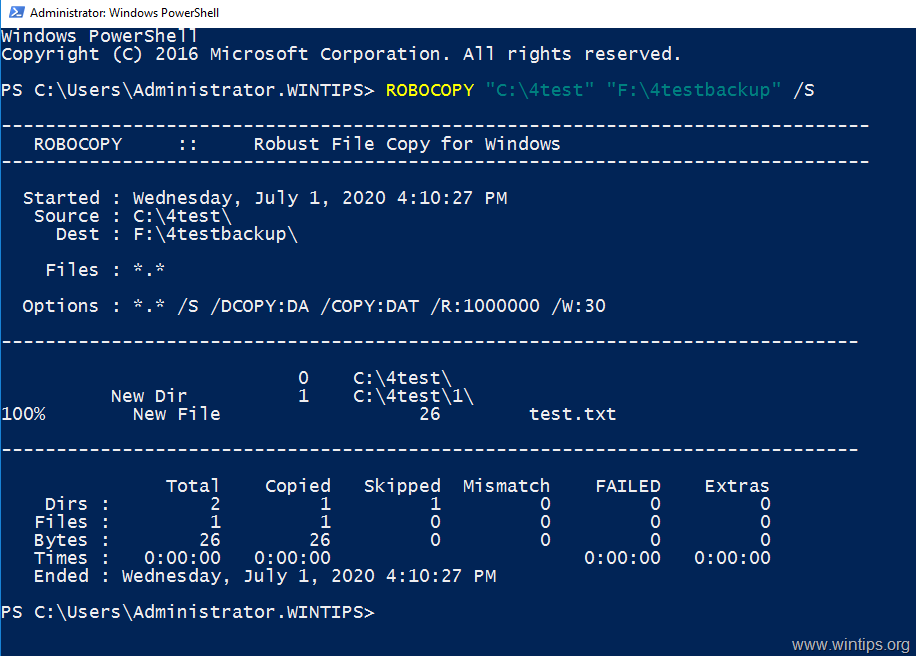
This command-line option allows you to update files that have changed.Ĭopies files from Source that exist on Destination only. If you do not include a MM-DD-YYYY value, xcopy copies all Source files that are newer than existing Destination files. Suppresses the display of xcopy messages.ĭisplays source and destination file names while copying.ĭisplays a list of files that are to be copied.Ĭreates decrypted Destination files when the destination does not support encryption.Ĭopies source files changed on or after the specified date only. Verifies each file as it is written to the destination file to make sure that the destination files are identical to the source files. Prompts you to confirm whether you want to create each destination file. This parameter can include a drive letter and colon, a directory name, a file name, or a combination of these.ĭisplays the following message and waits for your response before starting to copy files: Press any key to begin copying file(s) Specifies the destination of the files you want to copy. This parameter must include either a drive or a path. Specifies the location and names of the files you want to copy. Copies files and directories, including subdirectories.įor examples of how to use this command, see Examples.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
